The VESA Local Bus is a local bus defined by the Video Electronics Standards Association, mostly used in personal computers based on the Intel 80486 CPU. VESA Local Bus worked alongside the ISA bus; it acted as a high-speed conduit for memory-mapped I/O and DMA, while the ISA bus handled interrupts and port-mapped I/O.
The VESA Local Bus was designed as a stop-gap solution to the problem of the ISA buss limited bandwidth. VESA had several flaws that served to limit its useful life substantially: 80486 dependence. The VESA Local Bus relied heavily on the 80486s memory bus design. When the Pentium processor started to gain mass acceptance, circa 1995, there were major differences in its bus design, and the VESA bus was not easily adaptable. This also made moving the bus to non-Intel architectures nearly impossible. Few Pentium motherboards with VESA slots were ever made. Limited number of slots available. Most PCs that used VESA Local Bus had only one or two slots available, as opposed to 5 or 6 ISA slots. This was because, as a direct branch of the 80486 memory bus, the VESA Local Bus didnt have the electrical ability to drive more than 1 or 2 (or 3 at the most) cards at a time.
Despite these problems, the VESA Local Bus was very commonplace on 486 motherboards. Probably a majority of 486-based systems had a VESA Local Bus video card, although early 486 systems never had VESA slots, as VESA debuted years after the introduction of the 486 processor.
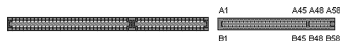
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | D1 | Data 1 |
| A2 | D3 | Data 3 |
| A3 | GND | Ground |
| A4 | D5 | Data 5 |
| A5 | D7 | Data 7 |
| A6 | D9 | Data 9 |
| A7 | D11 | Data 11 |
| A8 | D13 | Data 13 |
| A9 | D15 | Data 15 |
| A10 | GND | Ground |
| A11 | D17 | Data 17 |
| A12 | Vcc | +5 VDC |
| A13 | D19 | Data 19 |
| A14 | D21 | Data 21 |
| A15 | D23 | Data 23 |
| A16 | D25 | Data 25 |
| A17 | GND | Ground |
| A18 | D27 | Data 27 |
| A19 | D29 | Data 29 |
| A20 | D31 | Data 31 |
| A21 | A30 | Address 30 |
| A22 | A28 | Address 28 |
| A23 | A26 | Address 26 |
| A24 | GND | Ground |
| A25 | A24 | Address 24 |
| A26 | A22 | Address 22 |
| A27 | VCC | +5 VDC |
| A28 | A20 | Address 20 |
| A29 | A18 | Address 18 |
| A30 | A16 | Address 16 |
| A31 | A14 | Address 14 |
| A32 | A12 | Address 12 |
| A33 | A10 | Address 10 |
| A34 | A8 | Address 8 |
| A35 | GND | Ground |
| A36 | A6 | Address 6 |
| A37 | A4 | Address 4 |
| A38 | WBACK# | Write Back |
| A39 | BE0# | Byte Enable 0 |
| A40 | VCC | +5 VDC |
| A41 | BE1# | Byte Enable 1 |
| A42 | BE2# | Byte Enable 2 |
| A43 | GND | Ground |
| A44 | BE3# | Byte Enable 3 |
| A45 | ADS# | Address Strobe |
| A48 | LRDY# | Local Ready |
| A49 | LDEV | Local Device |
| A50 | LREQ | Local Request |
| A51 | GND | Ground |
| A52 | LGNT | Local Grant |
| A53 | VCC | +5 VDC |
| A54 | ID2 | Identification 2 |
| A55 | ID3 | Identification 3 |
| A56 | ID4 | Identification 4 |
| A57 | LKEN# | |
| A58 | LEADS# | Local Enable Address Strobe |
| B1 | D0 | Data 0 |
| B2 | D2 | Data 2 |
| B3 | D4 | Data 4 |
| B4 | D6 | Data 6 |
| B5 | D8 | Data 8 |
| B6 | GND | Ground |
| B7 | D10 | Data 10 |
| B8 | D12 | Data 12 |
| B9 | VCC | +5 VDC |
| B10 | D14 | Data 14 |
| B11 | D16 | Data 16 |
| B12 | D18 | Data 18 |
| B13 | D20 | Data 20 |
| B14 | GND | Ground |
| B15 | D22 | Data 22 |
| B16 | D24 | Data 24 |
| B17 | D26 | Data 26 |
| B18 | D28 | Data 28 |
| B19 | D30 | Data 30 |
| B20 | VCC | +5 VDC |
| B21 | A31 | Address 31 |
| B22 | GND | Ground |
| B23 | A29 | Address 29 |
| B24 | A27 | Address 27 |
| B25 | A25 | Address 25 |
| B26 | A23 | Address 23 |
| B27 | A21 | Address 21 |
| B28 | A19 | Address 19 |
| B29 | GND | Ground |
| B30 | A17 | Address 17 |
| B31 | A15 | Address 15 |
| B32 | VCC | +5 VDC |
| B33 | A13 | Address 13 |
| B34 | A11 | Address 11 |
| B35 | A9 | Address 9 |
| B36 | A7 | Address 7 |
| B37 | A5 | Address 5 |
| B38 | GND | Ground |
| B39 | A3 | Address 3 |
| B40 | A2 | Address 2 |
| B41 | n/c | Not connected |
| B42 | RESET# | Reset |
| B43 | DC# | Data/Command |
| B44 | M/IO# | Memory/IO |
| B45 | W/R# | Write/Read |
| B48 | RDYRTN# | Ready Return |
| B49 | GND | Ground |
| B50 | IRQ9 | Interrupt 9 |
| B51 | BRDY# | Burst Ready |
| B52 | BLAST# | Burst Last |
| B53 | ID0 | Identification 0 |
| B54 | ID1 | Identification 1 |
| B55 | GND | Ground |
| B56 | LCLK | Local Clock |
| B57 | VCC | +5 VDC |
| B58 | LBS16# | Local Bus Size 16 |
This section is currently based solely on the work by Mark Sokos.
This file is intended to provide a basic functional overview of the Vesa Local Bus, so that hobbyists and amateurs can design their own VLB compatible cards.
It is not intended to provide complete coverage of the VLB standard.
VLB Connectors are usually inline with ISA connectors, so that adapter cards may use both. However, the VLB is separate, and does not need to connect to the ISA portion of the bus.
The 64 bit expansion of the bus (optional) does not add additional pins or connectors. Instead, it multiplexes the existing pins. The 32 bit VLB bus does not use the 64 bit signals shown in the above pinouts.
Signal Descriptions
A2-A31
Address Bus
ADS
Address Strobe
BE0-BE3
Byte Enable. Indicates that the 8 data lines corresponding to each signal will deliver valid data.
BLAST
Burst Last. Indicates a VLB Burst Cycle, which will complete with *BRDY. The VLB Burst cycle consists of an address phase followed by four data phases.
BRDY
Burst Ready. Indicates the end of the current burst transfer.
D0-D31
Data Bus. Valid bytes are indicated by *BE(x) signals.
D/C
Data/Command. Used with M/IO and W/R to indicate the type of cycle.
| M/IO | D/C | W/R | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | INTA sequence |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | Halt/Special (486) |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | I/O Read |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | I/O Write |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Instruction Fetch |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Halt/Shutdown (386) |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Memory Read |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Memory Write |
ID0-ID4
Identification Signals.
| ID0 | ID1 | ID4 | CPU | Bus Width | Burst |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | (res) | ||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | (res) | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 486 | 16/32 | Burst Possible |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 486 | 16/32 | Read Burst |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 386 | 16/32 | None |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 386 | 16/32 | None |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | (res) | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 486 | 16/32/64 | Read/Write Burst |
| ID2 Indicates wait: | 0 = 1 wait cycle (min) |
| 1 = no wait | |
| ID3 Indicates bus speed: | 0 = greater than 33.3 MHz |
| 1 = less than 33.3 MHz |
IRQ9
Interrupt Request. Connected to IRQ9 on ISA bus. This allows standalone VLB adapters (not connected to ISA portion of the bus) to have one IRQ.
LEADS
Local Enable Address Strobe. Set low by VLB master (not CPU). Also used for cache invalidation signal.
LBS16
Local Bus Size 16. Used by slave device to indicate that it has a transfer width of only 16 bits.
LCLK
Local Clock. Runs at the same frequency as the cpu, up to 50 MHz. 66 MHz is allowed for on-board devices.
LDEV
Local Device: When appropriate address and M/IO signals are present on the bus, the VLB device must pull this line low to indicate that it is a VLB device. The VLB controller will then use the VLB bus for the transfer.
LRDY
Local Ready. Indicates that the VLB device has completed the cycle. This signal is only used for single cycle transfers. *BRDY is used for burst transfers.
LGNT
Local Grant. Indicates that an *LREQ signal has been granted, and control is being transferred to the new VLB master.
LREQ
Local Request. Used by VLB Master to gain control of the bus.
M/IO
Memory/IO. See D/C for signal description.
RDYRTN
Ready Return. Indicates VLB cycle has been completed. May precede LRDY by one cycle.
RESET
Reset. Resets all VLB devices.
WBACK
Write Back.
64-bit Expansion Signals
ACK64
Acknowledge 64 bit transfer. Indicates that the device can perform the requested 64 bit transfer cycle.
BE4-BE7
Byte Enable. Indicates which bytes are valid (similar to BE0-BE3).
D32-D63
Upper 32 bits of data bus. Multiplexed with address bus.
LBS64
Local Bus Size 64 bits. Used by VLB Master to indicate that it desires a 64 bit transfer.
W/R
Write/Read. See D/C for signal description.
64 Bit Data Transfer Timing Diagram:
Address Data
Phase Phase
_______ _______ _______
LCLK ___| |_______| |_______| |_______
____ ______________________________________
*ADS |_______|
_______________ _______________
A2-A31 ----<_______________><_______________>-------------
D34-D63 Address Data D34-D63
_______________ _______________
D/C ----<_______________><_______________>-------------
M/IO, W/R M/IO, W/R Data D32-33
_____ _____________________________
*LDEV |_______________|
_____ _____________________________
*LBS64 |_______________|
______ _____________________________
*ACK64 |______________|
_______________
D0-D31 --------------------<_______________>-------------
_____________________ _____________
LRDY |______________|



 correct
correct incorrect
incorrect